The rapid and delicate dedication of pathogenic micro organism is extraordinarily necessary in biotechnology, medical prognosis, and the present battle towards bioterrorism. Current strategies both lack ultrasensitivity or take a very long time for evaluation.
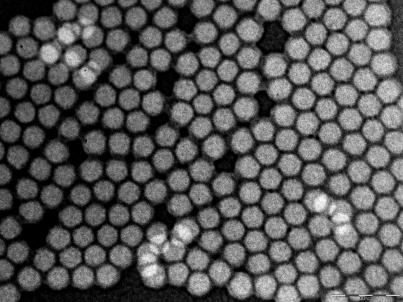
Here, we report a bioconjugated nanoparticle-based bioassay for in situ pathogen quantification all the way down to single bacterium inside 20 min.
The bioconjugated nanoparticle offers a particularly excessive fluorescent sign for bioanalysis and could be simply included with biorecognition molecules, resembling antibody. The antibody-conjugated nanoparticles can readily and particularly determine a wide range of bacterium, resembling Escherichia coli O157:H7, by means of antibody-antigen interplay and recognition. The single-bacterium-detection functionality inside 20 min has been confirmed by the plate-counting methodology and realized by using two unbiased optical strategies.
The two detection strategies correlated extraordinarily nicely. Furthermore, we have been in a position to detect a number of bacterial samples with excessive throughput by using a 384-well microplate format.
To present the usefulness of this assay, now we have precisely detected 1-400 E. coli O157 bacterial cells in spiked floor beef samples. Our outcomes display the potential for a broad software of bioconjugated nanoparticles in sensible biotechnological and medical purposes in varied biodetection programs.
The final energy of integrating bionanotechnology into advanced organic programs will emerge as a revolutionary software for ultrasensitive detection of illness markers and infectious brokers.
An perception into Australian nurses‘ expertise of withdrawal/withholding of remedy within the ICU.
BACKGROUNDThe success of biotechnology has created ethical and moral dilemmas regarding end-of-life care within the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). Whilst the competent particular person has the best to refuse or embrace remedy, ICU sufferers are not often in a position to train this proper. Thus, decision-making is left to medical professionals and household/important others.
OBJECTIVEThis research aimed to discover the lived expertise of ICU nurses caring for shoppers having remedy withdrawn or withheld, and enhance consciousness and understanding of this expertise amongst different well being professionals.
METHODSVan Manens‘ (1990) phenomenological framework fashioned the premise of this research because it supplied an in-depth perception into the human expertise.
A comfort pattern of ten ICU Nurses participated within the research. Conversations have been transcribed verbatim and analysed using a technique of thematic evaluation.RESULTSFive main themes emerged in the course of the evaluation. These have been: (1) consolation and care, (2) rigidity and battle, (3) do no hurt, (4) nurse-family relationships and (5) invisibility of grief and struggling.CONCLUSIONSThe expertise of offering care for the grownup having remedy withdrawn or withheld within the ICU represents a major private {and professional} battle.
Improvements in communication between well being professionals, debriefing and training in regards to the technique of withdrawing or withholding remedy could be useful to each workers and households and has the potential to enhance affected person care and scale back burden on nurses.
